Shopping Saturday – Tudor tradesmen of Great Dunmow
Genealogist Thomas MacEntee of Geneabloggers runs a great website for genealogists. He suggests ‘Daily Blogging Prompts’ to help inspire bloggers to write genealogical posts. In the spirit of one of his Prompts, Shopping Saturday, my blog today is about shopping (or rather tradesmen) in Tudor Great Dunmow.
The list of names for the 1525-6 collection for the church steeple contains some of the trades of Tudor Great Dunmow. It should be noted that the list is not a census in the modern terms of a census, and so the trade of a person was only recorded if two people had the same name. Thus the three John Parkers had their trade recorded alongside their name distinguish them from each other – John Parker the tiler, John Parker the wheeler and John Parker the fletcher. Trade (and occupations) within the parish, as documented within the 1525-6 collection for the steeple include
– church clerk
– dyer
– wheeler
– fletcher
– parish priest
– vicar
– retired vicar
– haberdasher
– butcher
– glover
(Obviously, this is not a complete list of the occupations of Tudor Great Dunmow, just a list where someone’s occupation had been recorded).
A ‘fletcher’ was an arrow-maker – a trade that evidently made John Parker, the Fletcher, a very wealthy man. His contribution to the church steeple was 26s 8d – a substantial amount of money. In further parish collections he contributed 18s 10d for the Great Bell, and 13s 4d for the church organ. In the 1523-4 Lay Subsidy returns for Great Dunmow, John Parker was assessed as having goods to the value of £105 13s 4d which resulted in him paying tax of 105s 8d. The Lay Subsidy returns show that he was the wealthiest man in the parish. However, despite his great wealth, in the list for the church steeple collection, John Parker, the fletcher, appears below the clergy and two lords of manors. Wealth wasn’t everything in this Tudor parish: the status of the elite meant more than the wealth and piety of tradesmen.
Being a fletcher in Tudor England was a very important trade. Throughout his reign, Henry VIII was, at various times, at war with either France or Scotland. Both Henry, and his father Henry VII, passed legislation to enforce that the men of Tudor England were reasonably proficient at the longbow. In 1515 Henry VIII imposed a Statue that all men, except ‘spiritual’ men, Justices and Barons, should practice shooting long bows. Bows and arrows had to be bought for all male children between the ages of 7 and 17. Henry also dictated that every city and town should have butts so that the men could practice their shooting their long bows at them.
 Luttrell Psalter, Psalm 79; Archers practicing at the butts (1325-35) (1)
Luttrell Psalter, Psalm 79; Archers practicing at the butts (1325-35) (1)
Throughout the Henrician churchwarden accounts there are numerous receipts for sums of money which was received for ‘shooting’ i.e. shooting longbows and arrows at a target. These ‘shooting’ games held in Great Dunmow and surrounding villages will be discussed in detail in future blog posts. For John Parker, fletcher of Great Dunmow, business must have been flourishing and profitably. We can only guess at how John Parker sold his arrows to his customers. Did they come ‘shopping’ to his workshop, and if they did, in the spirit of Geneabloggers’ Daily Prompt, was it on a Saturday?
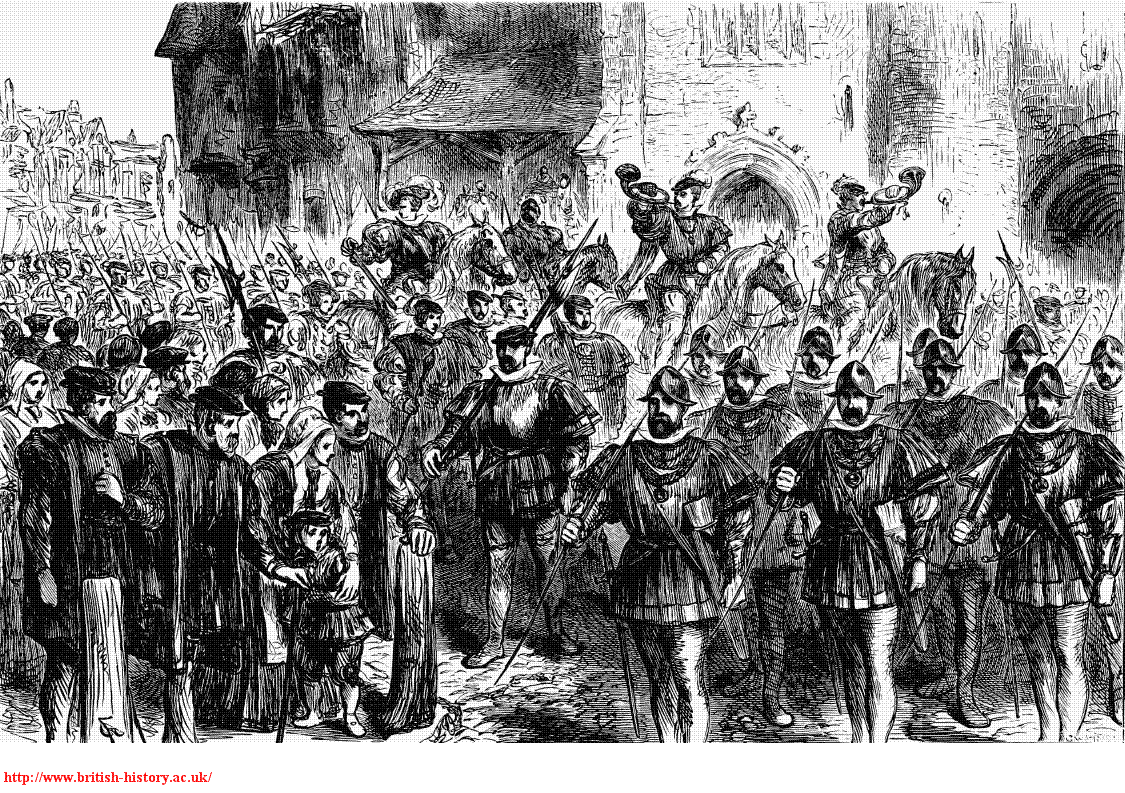
March of the Archers, Moorfields, City of London 1530 (2)
Footnotes
(1) Luttrell Psalter, Psalm 79 (East Anglia, England, 1325-35), shelfmark Add. 42130, f.147v, © British Library Board.
(2) Walter Thornbury, ‘Threadneedle Street’, Old and New London: Volume 1 (1878), pp.531-544. (Consulted online at british-history.ac.uk, date accessed January 2012).
(3) Weapons and war machinery, in Pseudo-Aristotle’s ‘About the Secrets of Secrets’ (1326-7), shelfmark: Additional MS 47680, f.43v, © British Library Board.
All digital images from the British Library’s Online Images archive appear by courtesy of the British Library Board and may not be reproduced (© British Library Board).
Notes about Great Dunmow’s churchwarden accounts
Great Dunmow’s original churchwardens’ accounts (1526-1621) are kept in Essex Record Office (E.R.O.), Chelmsford, Essex, D/P 11/5/1. All digital images of the accounts within this blog appear by courtesy of Essex Record Office and may not be reproduced. Examining these records from this Essex parish gives the modern reader a remarkable view into the lives and times of some of Henry VIII’s subjects and provides an interpretation into the local history of Tudor Great Dunmow.
*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
This blog
If you want to read more from my blog, please do subscribe either by using the Subscribe via Email button top right of my blog, or the button at the very bottom. If you’ve enjoyed reading this post, then please do Like it with the Facebook button and/or leave a comment below.
Thank you for reading this post.
You may also be interested in the following
– Index to each folio in Great Dunmow’s churchwardens’ accounts
– Great Dunmow’s Churchwardens’ accounts: transcripts 1526-1621
– Tudor local history
– Tudor trades and occupations
– Building a medieval church steeple
© Essex Voices Past 2012-2013.

